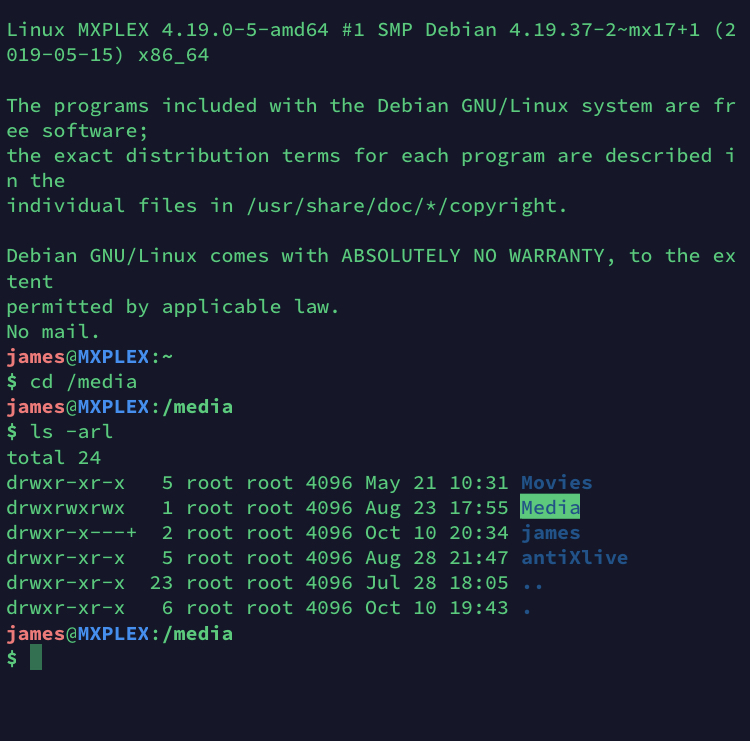
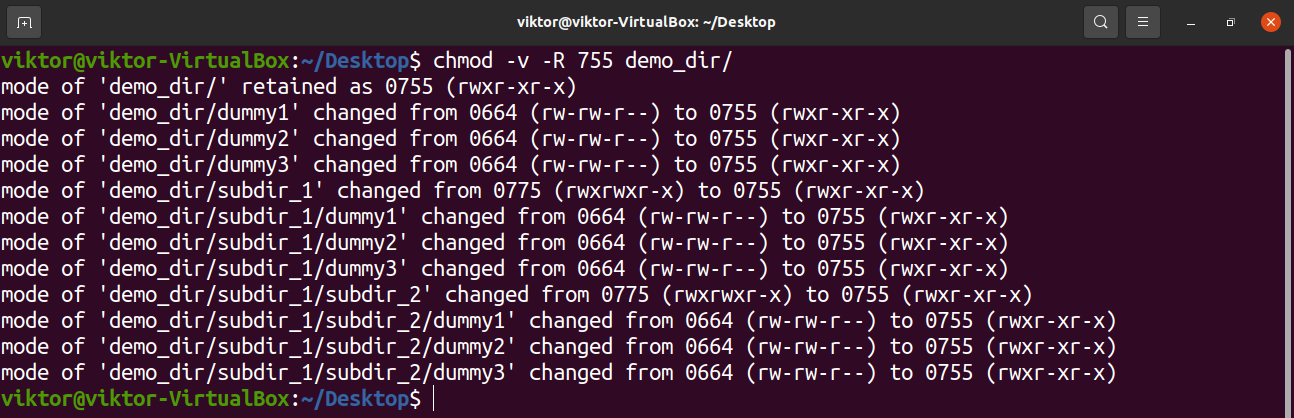
If you want to access the files or directories recursively in a specific directory, follow this command chmod R MODE DIRECTORY For a better understanding, have a look here chmod R 755 /var/www You can change the permissions of the files under the mentioned directory Further, it will Find All Directory or File (Recursively) Only And Execute Command (Chmod) linux ubuntu Apply chmod 755 to directory and subdirectories only (excluding files) find /mydir type d exec chmod 755 {} \;The group permission is 5 and others permission is 4 Therefore, the commands that use numbers to represent permissions arechmod 754 file For example, there's one in my directoryfile2File, current permissions arerwrr(644), now change torwxrxrx(755), execute the command $ chmod 755 file2You can Description of other parameters
3
Chmod 755 recursive command
Chmod 755 recursive command-Chmod x adds the execute permission for all users to the existing permissions chmod 755 sets the 755 permission for a file 755 means full permissions for the owner and read and execute permission for othersRecursively chmod 644 all files only (and ignore the directories) find type f exec chmod 644 {} \;




How To Recursively Change File Permissions In Linux Make Tech Easier
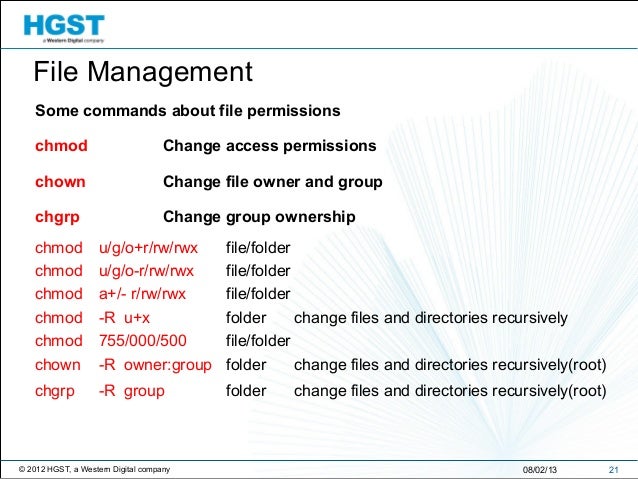
Examples chmod 644 filehtm Set the permissions of filehtm to "owner can read and write; Change Permission Recursively It is common to use the basic chmod command to change the permission of a single file However, you may need to modify the permission recursively for all files within a directory In such cases, the chmod recursive option (R or recursive) sets the permission for a directory (and the files it contains) Below are some examples of how to use the chmod command in symbolic mode Give the members of the group permission to read the file, but not to write and execute it chmod g=r filename;
find type f exec chmod 644 {} find type d exec chmod 755 {} I'm not sure of what they do when executed In theory I guess they go search of all the files and convert them to permissions 644 and the second line search for all the folders and convert them to 755 but I don't thing that I did anywhing once I typed enterChmod 755 Chmod 755 ( chmod arwx,gw,ow) sets permissions so that, (U)ser / owner can read, can write and can execute (G)roup can read, can't write and can execute (O)thers can read, can't write and can execute Owner Rights (u)This will find all files named filename, recursively from the current directory, and pass them to chmod find name filename xargs chmod 755 See the manpages for find and xargs for more advanced options In particular, look at the print0 flag and corresponding 0 to xargs if you get errors about files with spaces in the name
2,2 463 #2 Hello, It's generally advised to avoid using recursive chown or chmod commands For instance, it's possible a user has intentionally configured the permissions on a file/directory to something other than 0755 or 0644 Thank youJust select the appropriate permissions and it will tell you the permissions in both absolute and symbolic mode Change permission on all the files in a directory recursively chmod 777 Everything for everyone chmod x or chmod ax Execution for everyone chmod 755 Only owner can write, read and execute for everyone Allowing the cd, change directory, command to function properly Files are created as 644, one less than the directory This is because normal files do not need execution permissions Directories do, for cd So let's fix it with find and exec chmod Recursively with Find find type d exec chmod 755{} \;




40 Best Examples Of Find Command In Linux




Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org
If you allow directory listings, then use 755 If you want something less invasive, then just remove the write bits for group and "other" I think 644 is standard for files and 755 for directories Does chmod recursively?Chmod directory recursive To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the R, (recursive) option The general syntax to recursively change the file's permissions is as follows Please refer to the manual (man chmod)R, recursive change files and directories recursively chmod R 755 /path/to/directory wouldBut I was wondering How to do it in one line using find and excluding the directories and Which method is better, find exec or xargs?




How To Recursively Change File Permissions In Linux Make Tech Easier




How To Recursively Change File Permissions In Linux Make Tech Easier
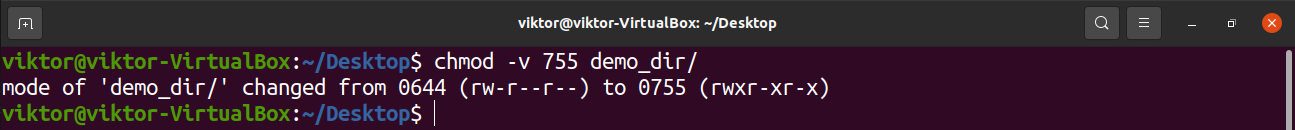
Using the R (recursive) option, you can give recursively permissions to all files and directories inside a specific directory chmod R MODE DIRECTORY For example, to change the permissions of all files and subdirectories under the /var/www directory to 755 you would use chmod R 755 /var/www Changing File Permissions in Bulk# The syntax for changing the file permission recursively is chmod R permission directory Therefore, to set the 755 permission for all files in the Example directory, you would type sudo chmod R 755 Example The command gives read, write, and execute privileges to the owner (7) and read and execute access to everyone else (55)Group members and other users can read and execute,




Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do Codefather




How To Recursively Change The File S Permissions In Linux Unihost Faq
The other way is terminal , where you can change the permission via Chmod If you use chmod 777 that means you assigned all the permissions ie to make file readable, writable and executable by everyone chmod 775 /path/to/file chmod command uses & Explanation chmod is a command to change permission of a file It stands for change modeChmod g= filename The chmod command supports a recursive option For example, to add read permissions for user, group, and other recursively on a directory and its subdirectories and files recursively , use chmod R ar Remember, too, that likePosted (5 days ago) Chmod Recursive # The chmod command means that you can change the permissions of recordsdata utilizing symbolic or numeric mode To recursively function on all recordsdata and directories below a given listing, use the chmod command with the R, (–recursive) choice




How To Apply Chmod Recursively



Chmod Recursive Files Only
$ chmod 755 footxt $ chmod x quickrefpy $ chmod ux quickrefpy $ chmod u=rwx,g=rx,o= quickrefsh #Change files and directories recursively $ chmod R 755 my_directory The chmod command stands for "change mode" #Apply chmod 644 to all files only (excluding directory)Group can read only;



Solved Question 1 Which Command Will Find All Items Under Chegg Com




Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech
For example, to change the permissions of all files and subdirectories under the /var/www directory to 755 you would use $ chmod R 755 /var/www Operating on Symbolic Links Symbolic links always have 777 permissions By default, when changing symlink's permissions, chmod will change the permissions on the file the link is pointing to$ find /var/www type d exec chmod u=rwx,g=rx,o=rx {} \;Recursively remove the write permission for other users chmod R ow dirname



Common Bash Commands




Introduction To The Linux Chmod Command Opensource Com
How do I run chmod 777?Find type f exec chmod 644 {} \;To apply chmod 755 to all the subsequent files and directories, run chmod in recursive mode $ chmodv R 755 < file_or_directory > Verify the changes using the ls command




Linux Command Line Cheat Sheet Kalitut




New Bash Linux Cheat Sheet Wallpaper Download Free 40 X 3050px
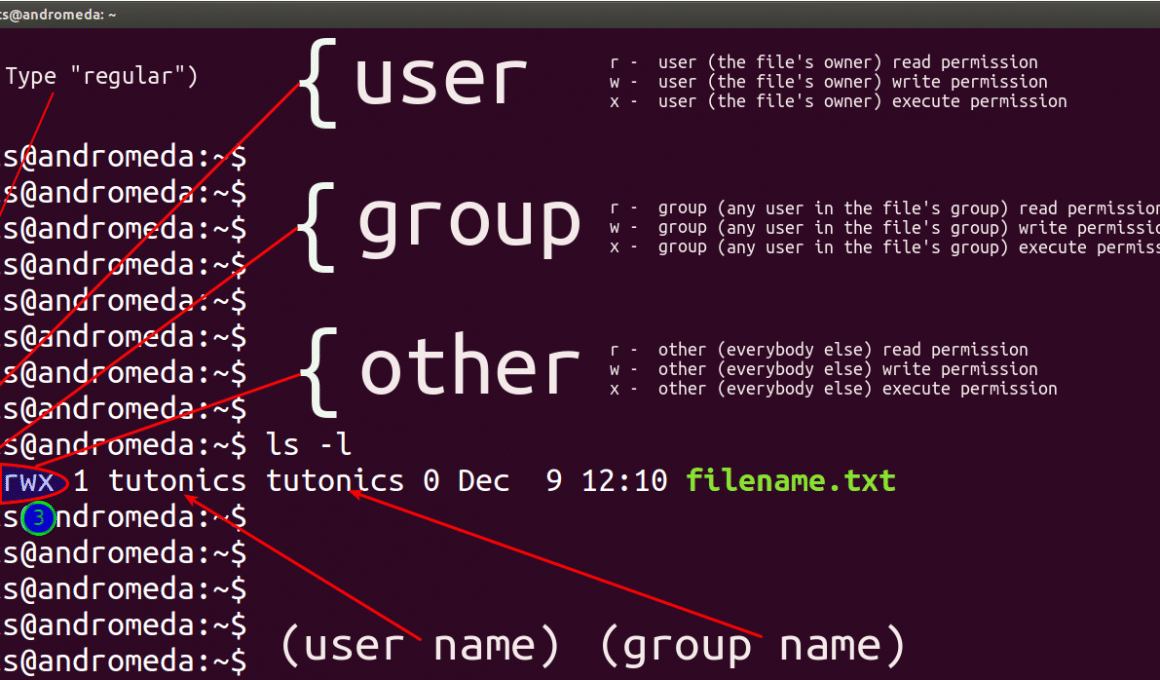
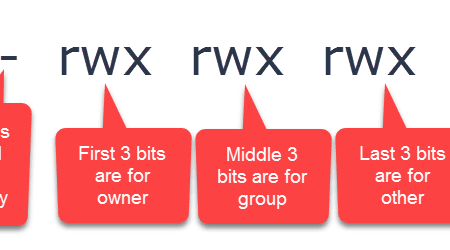
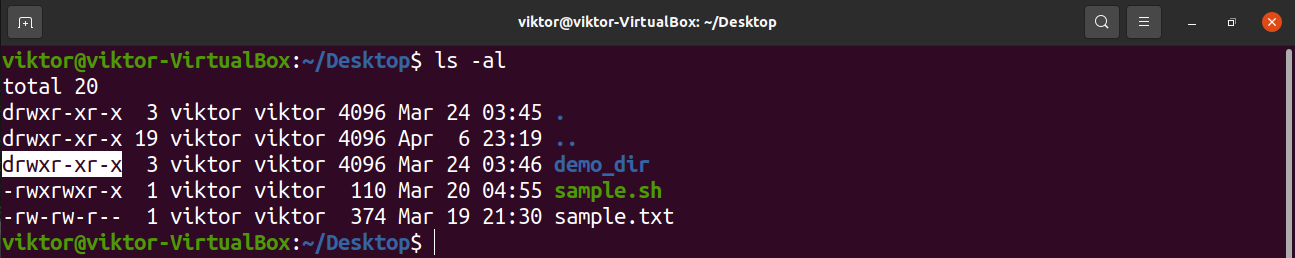
I was trying to chmod folders and files with find type d exec chmod 755 {} \;To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions Following is a sample of ls l command output In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents the permissions for the 3 types of users rwrr 1 john john 272 Mar 17 02 testtxt In the above example User (john) has read and write permissionRemove the execute permission for all users chmod ax filename;



Why Would Using Chmod 777 Recursively From The Root Cause A Linux Box To Not Boot I Could Understand This If I Were Limiting Permissions But Why Would Adding Permissions Cause This




Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do By Claudio Sabato Medium
# chmod 755 testtxt # ls l testtxtrwxrxrx 1 root root Jun 17 11 test2txt Changing permissions on a directory chmod OCTALMODE DIR – This example shows how us changing the permissions on a directory named php # chmod 755 php mode of `php' changed to 0777 (rwxrwxrwx) # ls l drwxrwxrwx 3 root root 40K php/ The command chmod 755 file is equivalent to chmod 0755 file If we run this command on a file which has the SETUIDbit or SETGIDbit set, it will remove the SETUID/SETGIDbit chmod x file will leave the SETUID/SETGIDbit untouched We can see this in the following exampleChmod commandIn this article, I'll share with you some of the practical examples of chmod command I'll also explain some the popular terms like chmod 777 or chmod 755 or chmod rBefore you see the chmod examples, I would strongly advise you to learn the basics of file permissions in Linux Using chmod command will be a lot easier once you




How To Recursively Change File Permissions In Linux Make Tech Easier




Linux Chmod Recursive How To Change File Permissions Recursively
Find type f exec chmod 644 {} \; The correct recursive command is sudo chmod R 755 /opt/lampp/htdocs Note R should be before 755 – Sandip Patel SM Oct 11 '17 at 737 1 should be edited, doesn't work on mac osx without pedantic syntaxNote if you need a complete guide on the chown command, we wrote an extensive one about file permissions on Linux Chown User and Group How to recursively change the permissions of a file?




Linux Commands Chmod




File And Directory Permissions In Linux Freebsd Masos Tech
The chmod command with the R options allows you to recursively change the file's permissions To recursively set Use find /opt/lampp/htdocs type d exec chmod 755 {} \;if the number of files you are using is very large The type xoption searches for specific type of file only, where d is used for finding directory, f for file and l for link Use chmod 755 $(find /path/to/base/dir type d)otherwiseChange Specific File Names and Extension Permission Recursively You may need to change files permission recursively according to their names or permission The find command can be used for specific file names and extensions




Chmod Command In Ubuntu 04 How It Works




How Can I Recursively Change The Permissions Of Files And Directories Ask Ubuntu
If you specify the h flag, the chmod command prevents this mode change If you specify both the h flag and the R flag, the chmod command descends the specified directories recursively, and when a symbolic link is encountered, the mode of the file or directory pointed to by the link is $ find /var/www type d exec chmod 755 {} \;Chmod recursive This would recursively change the permission of all files and dir under / which can also destroy your system In such case it is always recommended to use # chmod changes recursive preserveroot 755 / chmod it is dangerous to operate recursively on '/' chmod use nopreserveroot to override this failsafe




Linux How To Recursively Chmod Only Directories And Not Files Chillzee Com



Understanding Linux File Permissions 755 And Rwxr Xr X Datamounts
What is chmod 755 command in Linux?If you want to recursively change the permissions of all the files within a directory, use $ chmod –R {permissions} {filename} This command gives the owner all three permissions and groups and others no permissions If you want to know more about chmod, use $ man chmod This will take you to the manual that has all the details on this command The find command can be used to find files and directories The chown command can be used to change user and group permission chmod Command Example In this example, you are setting permission to 0755 $ chmod R 0755 directoryNameHere However, if you need to apply conditional file permissions recursively, you need to use combination of the




This Chmod Calculator Makes Creating Chmod Commands A Cakewalk Hongkiat




9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux
Others can read only" chmod R 755 myfiles Recursively (R) Change the permissions of the directory myfiles, and all folders and files it contains, to mode 755User can read, write, and execute; chmod R 755 /var/www/html The mode can also be specified using the symbolic method chmod R u=rwx,go=rx /var/www/html Only root, the file owner, or user with sudo privileges can change the permissions of a file Be extra careful when recursively changing the files' permissions Using the find Command #These will recursively search the directory tree, starting at the current directory ('dot') Recursively chmod 755 all directories only find type d exec chmod 755 {} \;



What Is The Meaning Of Chmod 755 And How To Execute And Verify It




Linux Permissions Making Sense Of 755 And Rwxr Xr X Serverwise
Sticky Bit Use the octal CHMOD Command chmod R 655 folder_name OR use the symbolic CHMOD Command chmod R arwx,ux,gw,ow folder_name




Write A Unix Linux Find Like Command Myfind In Chegg Com



Chmod Not Working Software Web Applications Lawrence Systems Forums




Chmod 755




Engineering Secure Software Ppt Download



3




How To Recursively Change The File S Permissions In Linux Linuxize




Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples




Chmod 755 775 Recursive Ssh Permissions Chmod 775 Vs 777




Javarevisited 10 Examples Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux




Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize




Difference Between Locate Which And Find Command In Linux Geeksforgeeks




How To Set Chmod 777 To A Folder And All Its Contents Dev Community



Fastest Chmod 755 Recursive Folder




How To Recursively Change The File S Permissions In Linux Linuxize



Using Chmod X Command On Linux And Unix With Examples Systemconf




How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux




Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode




Linux Chmod Command Examples Journaldev



1




How To Set Chmod 777 To A Folder And All Its Contents Dev Community



Decoded Chmod Coreutils Maizure S Projects




Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples



Linux Chmod Recursive How To Change File Permissions Recursively




How To Recursively Change The File S Permissions In Linux Linuxize




The Chmod Command And Linux File Permissions Explained




Why Not To Use Chmod 777 Pi My Life Up



How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux




Fastest Chmod 755 Recursive



What Is The Meaning Of Chmod 755 And How To Execute And Verify It




Basic Linux Commands Coolguides



Tech It Easy Chmod Calculator Built With Angularjs And Material Design



How To Set File Permissions On A Mac Macinstruct



Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders




Command Line Quick Tips More About Permissions Fedora Magazine




The Chmod Command




Linux Chmod Command Dracula Servers Tutorials




How To Change Bulk File Permissions Recursively 2daygeek



What Is The Meaning Of Chmod 755 And How To Execute And Verify It




How To Change Permissions In Linux With Chmod Recursive




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




How To Set Chmod 777 To A Folder And All Its Contents Dev Community
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)



How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux




Chmod Recursively Change Files And Folders Permissions Recursively In Linux Linuxtect




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




How To Recursively Change The File S Permissions In Linux Unihost Faq




Your Question How Do I Set Full Permissions Chmod 777 In Ubuntu




How To Change Permissions In Linux



Recursive Chown Is Really Slow Issue 3 Docker For Linux Github




How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line



1



What Is The Meaning Of Chmod 755 And How To Execute And Verify It




Best Linux Chmod Command With Examples It Smart Tricks



Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
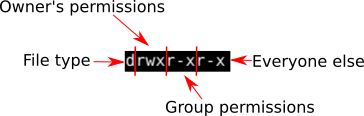



Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples




How To Apply Chmod Recursively With Best Practices Examples Golinuxcloud




Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions




Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders




Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples



Chmod Command




What Does 755 Permissions Mean In Unix




Directory How Can I Change Permissions Of A Folder Including Its Enclosed Files And Subdirectories Ask Ubuntu




Quick Answer How To Use Chmod In Linux Os Today




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices




Chmod Wiki Ask Ubuntu




How To Chmod Recursively In Linux Youtube
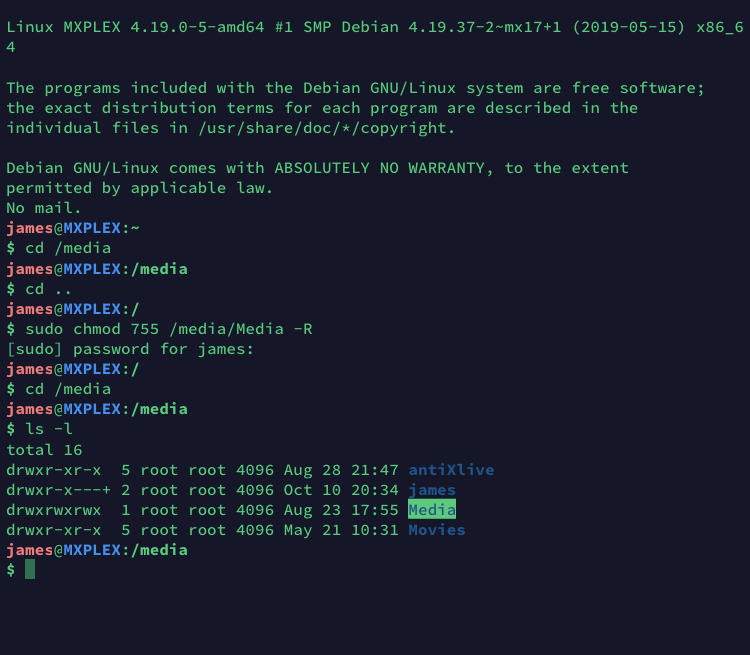



Chmod Not Working Software Web Applications Lawrence Systems Forums
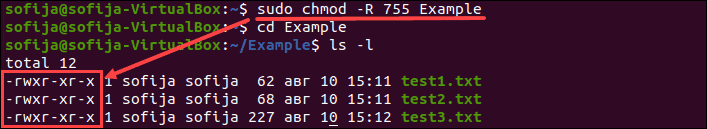



How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux




What Is Chmod 777 Poftut




Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Tecnstuff
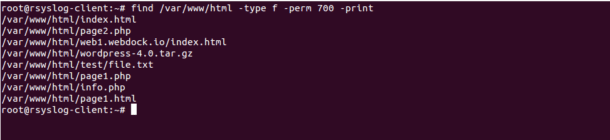



Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders




Basic Linux Commands Grep Pattern Files Search For Pattern In Files S Directory Listing S Al Formatted Listing With Hidden Files Cd Dir Change Directory To Dir Cd Change To Home Pwd




How To Recursively Change File Permissions In Linux Make Tech Easier




Chmod And Chown For Wordpress




Lo Mas Rapido Linux Chmod R 755 Recursive
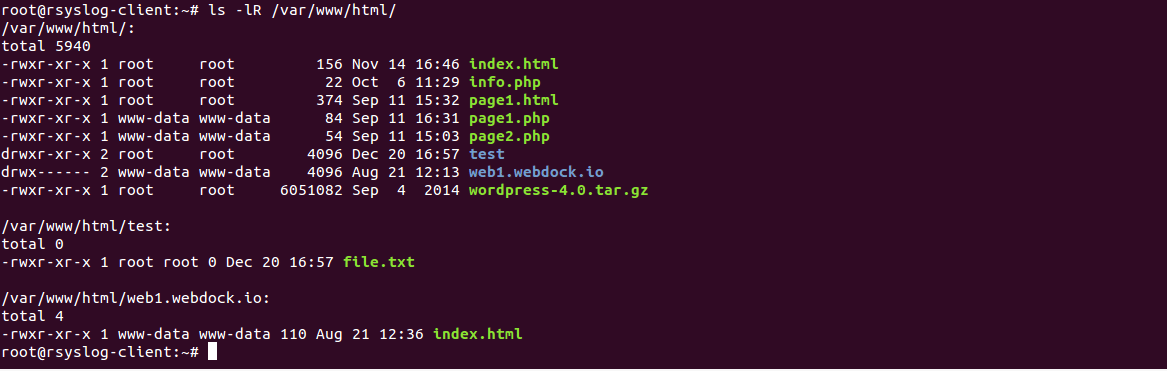



Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders


